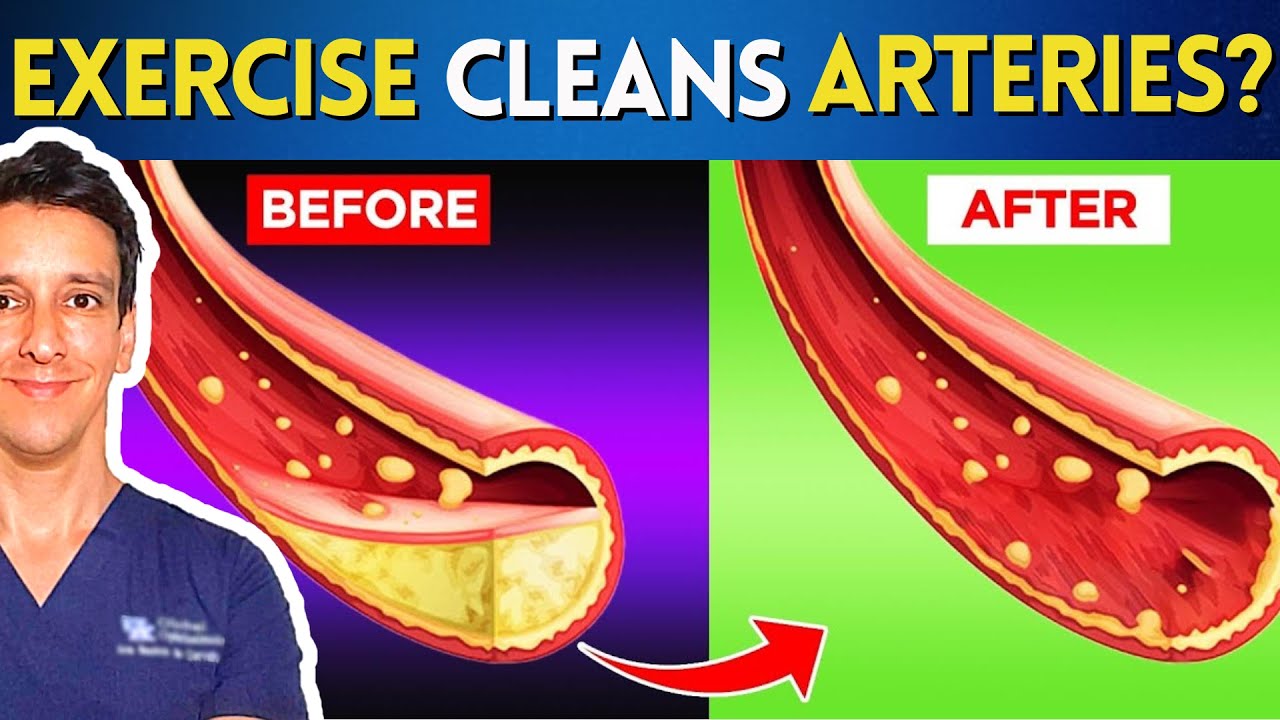
You’ve stumbled upon some groundbreaking information about how exercise can effectively reduce plaque in your arteries. The new trial showcased in the video by Nutrition Made Simple proves that supervised exercise, particularly high-intensity interval training (HIIT), can lead to a significant decrease in plaque size. By engaging in this specially designed exercise program, patients experienced a 1.2% drop in the largest plaque segment, hinting at the potential for reduced risk of heart-related events like heart attacks or strokes.
This study delved into the impact of exercise on high-risk patients with existing plaque in their arteries, offering a glimmer of hope for those looking to reverse heart disease. While traditional medical treatments can control lipid levels, the addition of exercise like HIIT showed promising results in shrinking plaque, highlighting the importance of incorporating physical activity into your health regimen. Take this valuable insight as a reminder to prioritize your cardiovascular health and explore the benefits of supervised exercise programs like HIIT for your overall well-being.
Summary of the New Trial
In this recent trial, a high-intensity interval training (HIIT) protocol was utilized to assess its impact on reducing plaque buildup in the arteries. Participants were enrolled in a supervised exercise program where plaque reduction was measured after a period of six months.
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) protocol used
The trial focused on the HIIT exercise regimen, which involves alternating periods of intense activity with short recovery periods. This form of workout is known for its effectiveness in improving cardiovascular health and fitness levels.
Supervised exercise program details
Participants underwent a structured HIIT program that involved treadmill or stationary bike workouts. The sessions consisted of warm-up, high-intensity intervals, recovery periods, and cool-downs, all overseen by professional trainers.
Plaque reduction in arteries measured after 6 months
After six months of following the supervised exercise program, the researchers measured the plaque in the arteries to evaluate any changes. The intervention group, which participated in the HIIT program, showed a significant reduction in plaque size compared to the control group.
Comparison of Control Group vs. Intervention Group
The trial compared the outcomes of two groups – the control group received standard care advice while the intervention group followed the supervised exercise program.
Standard care advice for control group
The control group received typical care advice, including recommendations for a healthy diet, regular exercise, not smoking, and managing blood pressure and glycated hemoglobin levels.
Supervised exercise program for intervention group
On the other hand, the intervention group engaged in the HIIT exercise program, highlighting the effectiveness of this high-intensity interval training in reducing plaque size significantly.
Significant reduction in plaque size for intervention group
The key finding of the trial was the noteworthy decrease in plaque size observed in the intervention group that participated in the HIIT program, showcasing the positive impact of this supervised exercise regimen.
Significance of Plaque Reduction
The study delved into the implications of the reduction in plaque size and its potential effects on overall heart health.
Discussion on 1.2% reduction in plaque size
The trial revealed a 1.2% reduction in plaque size in the arteries of participants following the HIIT program, prompting discussions on the significance of this decrease in relation to cardiovascular health.
Reference to lipid lowering treatment and risk reduction
By referencing other studies on lipid-lowering treatments, researchers highlighted the potential risk reduction associated with even small reductions in plaque size, emphasizing the importance of such interventions.
Evaluation of meaningful reduction in plaque size
The trial findings suggest that even modest reductions in plaque size can lead to substantial improvements in cardiovascular health outcomes, underscoring the importance of actively managing plaque buildup.
Structural Changes in Plaque
Researchers also examined the structural changes in plaque to better understand its stability and implications for heart health.
Importance of plaque composition and structure
Understanding the composition and structure of plaque is crucial in assessing its stability and the potential risks associated with ruptures or blockages.
Stability of plaque vs. reduction in thickness
While reducing plaque thickness is important, the study highlighted the significance of maintaining plaque stability to prevent adverse cardiovascular events.
Potential implications of plaque ‘shrinking’ on stability
The trial raised questions about how plaque shrinking, particularly through exercise interventions like HIIT, may influence the overall stability and long-term health of the arteries.
Impact of Different Types of Exercise on Plaque
Researchers also explored the effects of various types of exercise, such as cardio, weight training, and sports, on plaque reduction.
Cardio vs. weights vs. sports for plaque reduction
While the study focused on HIIT, further research is needed to investigate how different forms of exercise impact plaque size and composition.
HIIT protocol as the focus of the trial
The emphasis on the HIIT protocol in the trial highlights its effectiveness in reducing plaque size, but more studies are necessary to compare it with other exercise modalities.
Need for further research on varied exercise effects
The need for additional research to understand how different types of exercise influence plaque buildup and cardiovascular health outcomes was underscored in the study.
Relationship between Exercise and Plaque Reduction
The trial explored the correlation between exercise, weight loss, and the reduction in plaque size, as well as the impact of biomarkers like glycated hemoglobin and cholesterol levels.
Correlation between weight loss and plaque reduction
The study suggested that weight loss resulting from exercise may contribute to the reduction in plaque size, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a healthy weight for heart health.
Impact of glycated hemoglobin and cholesterol levels on plaque size
While some biomarkers remained unchanged between the groups, the reduction in plaque size in the HIIT group indicated that factors beyond lipid levels may play a role in improving cardiovascular health.
Different outcomes between HIIT group and control group
By comparing outcomes between the group following the HIIT program and the control group, researchers identified mechanisms through which exercise interventions can lead to plaque reduction.
Quality of Lipid Lowering Treatment in Combination with Exercise
The study highlighted the importance of consistently administering lipid-lowering treatments alongside exercise interventions to optimize cardiovascular health outcomes.
Consistent lipid-lowering treatment for all participants
All participants in the trial were on lipid-lowering treatments, emphasizing the necessity of maintaining such treatment regimens to effectively manage plaque buildup.
Relationship between LDL cholesterol levels and plaque reduction
Despite consistent LDL cholesterol levels across groups, the reduction in plaque size in the exercise group demonstrated the additive effects of exercise and lipid-lowering treatments.
Discussion on regression of plaque based on lipid levels
The findings underscored the potential for regression of plaque with a combination of lipid-lowering treatments and exercise regimens, showcasing the importance of holistic approaches to cardiovascular health.
Future Research Directions
The study provided insights into the potential for combined approaches involving exercise and lipid-lowering treatments and identified areas for future investigation.
Considerations for combined approach of lipid lowering and exercise
Researchers suggested exploring the combined effects of lipid-lowering medications and exercise programs to maximize the benefits of both interventions.
Potential additive effects of interventions
The notion of additive effects between lipid-lowering treatments and exercise interventions raises questions about the synergies that could enhance plaque reduction and cardiovascular health.
Questions for future studies and research
As the field of cardiovascular research evolves, the study highlighted the need for further investigations to elucidate the mechanisms underlying exercise-induced plaque reduction and its implications for heart health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the new trial shed light on the effectiveness of exercise, particularly high-intensity interval training, in reducing plaque buildup in the arteries. The findings have significant implications for heart health and underscore the importance of understanding the nuanced aspects of plaque reduction research for future advancements in cardiovascular care.