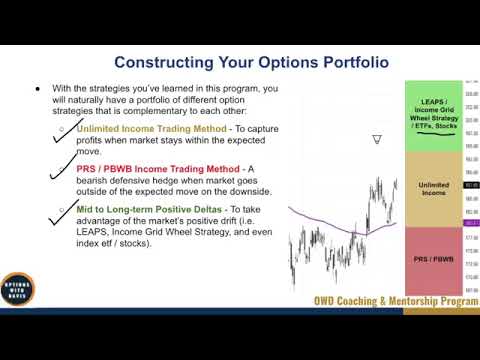
In the video “4-6 Constructing Your Options Portfolio” by Heating & Cooling Solutions, you will learn about the process of constructing an options portfolio. The portfolio consists of various option strategies, including the unlimited income trading method for capturing profits within the expected range, the put ratio spread and put broken wing butterfly methods as a bearish defensive hedge when the market goes outside the expected range on the downside, and a mid to long-term positive Delta portfolio consisting of leaps income grid real strategy, index ETFs, and stocks. The allocation of funds to each strategy depends on individual preferences and outlook on the market. By understanding these different strategies and their complementarity, you can create a holistic portfolio to take advantage of various market scenarios.
Understanding Options
What are options?
Options are financial instruments that provide the buyer with the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price within a specified period of time. These assets can include stocks, indices, commodities, and currencies.
Options offer flexibility and can be used for various purposes, such as hedging, speculation, and income generation. They are popular among traders and investors due to their potential for high returns and limited risk.
Call options
A call option gives the holder the right to buy an asset at a specified price, known as the strike price, within a specific time frame. If the price of the underlying asset rises above the strike price, the call option can be exercised, allowing the holder to buy the asset at a lower price and potentially profit from the price difference.
Call options are typically used by traders who anticipate the price of the underlying asset to increase. By purchasing call options, they can participate in the potential upside of the asset without actually owning it.
Put options
Put options, on the other hand, give the holder the right to sell an asset at a specified price within a specific time frame. If the price of the underlying asset falls below the strike price, the put option can be exercised, allowing the holder to sell the asset at a higher price and potentially profit from the price difference.
Put options are commonly used as a form of insurance or protection against a decline in the value of the underlying asset. Traders who anticipate a drop in the price of an asset may purchase put options to hedge their existing positions or speculate on the downside potential.
Option contracts
Options are traded in the form of contracts, with each contract representing a specific quantity of the underlying asset. The contract specifies the strike price, expiration date, and the type of option (call or put).
Option contracts can be bought and sold on options exchanges, and their prices are determined by various factors, including the current price of the underlying asset, volatility, time remaining until expiration, and interest rates.
Options trading strategies
Options trading involves the use of various strategies to maximize profits and minimize risk. These strategies can be classified based on the market outlook, risk tolerance, and investment goals of the trader or investor.
Some common options trading strategies include:
- Bullish market strategies: These strategies are used when the trader expects the price of the underlying asset to increase.
- Bearish market strategies: These strategies are used when the trader expects the price of the underlying asset to decrease.
- Neutral market strategies: These strategies are used when the trader expects the price of the underlying asset to remain relatively unchanged.
- Volatility strategies: These strategies are used when the trader expects an increase or decrease in market volatility.
By understanding different options trading strategies, individuals can tailor their trading approach to suit their preferences and market conditions.
Building Your Options Portfolio
Building a diversified options portfolio involves several steps to ensure it aligns with your investment goals, risk tolerance, and market outlook.
Step 1: Define your investment goals
Before constructing your options portfolio, it’s essential to define your investment goals. Are you aiming for income generation, capital appreciation, or a combination of both? Clarifying your objectives will help guide your decision-making process and the selection of suitable option strategies.
Step 2: Determine risk tolerance
Understanding and assessing your risk tolerance is crucial in options trading. Options can provide opportunities for significant returns, but they also carry inherent risks. Determine how much risk you are willing to take and consider your financial situation and investment experience when selecting option strategies.
Step 3: Assess market outlook
Evaluate the current market conditions and identify potential trends or events that may impact the performance of the underlying assets. Based on your analysis, determine your outlook for the market, whether it’s bullish, bearish, or neutral. This assessment will influence your selection of option strategies.
Step 4: Choose option strategies
Based on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and market outlook, select option strategies that align with your objectives. Consider strategies that suit different market conditions, such as bull spreads, bear spreads, iron condors, or straddles. Each strategy has its own risk-reward profile and profit potential.
Step 5: Allocate funds
Allocate funds in your options portfolio to different strategies based on your risk appetite and confidence in the strategies. Consider diversifying your portfolio by allocating funds to a mix of strategies that have varying levels of risk and profit potential. Remember to regularly review and adjust your allocations to adapt to changing market conditions.
By following these steps and carefully constructing your options portfolio, you can manage risk and potentially achieve your investment goals.
Option Strategies for Different Market Conditions
Options trading strategies can be categorized based on different market conditions. Here are some strategies commonly used in different market environments:
Bullish market strategies
Bullish market strategies are used when traders expect the price of the underlying asset to increase. These strategies aim to profit from upward price movements. Examples of bullish strategies include buying call options, bull spreads, and the long call butterfly.
Bearish market strategies
Bearish market strategies are used when traders expect the price of the underlying asset to decrease. These strategies aim to profit from downward price movements. Examples of bearish strategies include buying put options, bear spreads, and the long put butterfly.
Neutral market strategies
Neutral market strategies are used when traders expect the price of the underlying asset to remain relatively unchanged. These strategies aim to profit from low or no price movement. Examples of neutral strategies include iron condors, butterflies, and calendar spreads.
Volatility strategies
Volatility strategies are used when traders expect an increase or decrease in market volatility. These strategies aim to profit from changes in volatility levels. Examples of volatility strategies include straddles, strangles, and the VIX spread.
By understanding and utilizing these different strategies, traders can adapt to different market conditions and potentially generate profits.
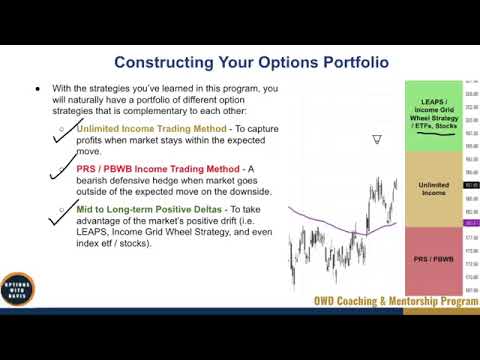
Unlimited Income Trading Method
The unlimited income trading method is a strategy designed to capture profits when the market stays within the expected range. This strategy can be used to generate consistent income over time. Here is an overview of the strategy and its key components:
Overview of the strategy
The unlimited income trading method involves selling out-of-the-money options on a regular basis to generate income. By selling options, traders collect premiums, which act as a source of income. The goal is for the options to expire worthless or to be bought back at a lower price, allowing the trader to keep the premium.
Capturing profits within expected market range
To capture profits within the expected market range, traders select strike prices for the options they sell that are outside of the expected move. This allows them to collect higher premiums while reducing the likelihood of the options being exercised.
Selecting suitable option contracts
When selecting option contracts for this strategy, traders consider the time decay (theta) and implied volatility. Options with a shorter time until expiration tend to have higher theta, meaning their value decreases more rapidly over time. Additionally, options with higher implied volatility tend to have higher premiums, providing more income-generating potential.
Position management techniques
Managing positions in the unlimited income trading method involves continuously monitoring and adjusting trades as needed. Traders may choose to roll their options positions forward, close positions early, or adjust strike prices to adapt to changing market conditions.
By implementing the unlimited income trading method, traders can generate consistent income while managing risk and maintaining a focused approach to options trading.
Put Ratio Spread
The put ratio spread is a strategy used as a bearish hedge when the market goes outside of the expected range on the downside. Here is an overview of the strategy and its key components:
Understanding the put ratio spread strategy
The put ratio spread involves buying a certain number of puts with a higher strike price and selling a greater number of puts with a lower strike price. This strategy profits from a decrease in the price of the underlying asset.
Using put options as a bearish hedge
Put options provide the right to sell an asset at a specific price, making them suitable for hedging against downside risk. By engaging in a put ratio spread, traders can limit potential losses in case the market falls below the expected range.
Calculating the ratio spread
The ratio spread is calculated by dividing the number of puts sold by the number of puts bought. The selected ratio can determine the risk-reward profile of the strategy. A higher ratio can provide more potential profit, but it also increases the risk.
Risks and rewards of the strategy
The put ratio spread has limited risk and potentially unlimited profit. The maximum profit occurs if the price of the underlying asset falls below the lower strike price. However, if the price rises above the higher strike price, the losses can be significant. It is crucial to monitor and manage positions to mitigate potential risks effectively.
By utilizing the put ratio spread as a bearish hedge, traders can protect their portfolios against downside risks while potentially benefiting from falling prices.
Put Broken Wing Butterfly
The put broken wing butterfly is a defensive hedge against downside risks. It combines elements of the put ratio spread and the butterfly spread to provide protection and potential profit. Here is an overview of the strategy and its key components:
Overview of the put broken wing butterfly strategy
The put broken wing butterfly involves buying a put option with a higher strike price, selling two put options with lower strike prices, and buying another put option with an even lower strike price. This strategy is used when the trader expects significant downside movement in the price of the underlying asset.
Defensive hedge against downside risks
The put broken wing butterfly provides a defensive hedge by limiting potential losses if the price of the underlying asset falls significantly. The strategy profits from a moderate downward movement in the price, while the lower strike put options provide protection against larger declines.
Setting up the butterfly spread
Setting up the put broken wing butterfly involves selecting suitable strike prices and the number of options bought and sold. The broken wing aspect of the strategy adds an asymmetrical profit potential, allowing traders to potentially generate more profit if the price falls within a specific range.
Managing the position
Managing the put broken wing butterfly position involves adjusting strikes and ratios as market conditions change. Traders may choose to roll positions forward, close positions early, or adjust the number of options to adapt to evolving market dynamics.
By utilizing the put broken wing butterfly strategy, traders can protect their portfolios against downside risks while potentially generating profits in specific price ranges.
Positive Delta Portfolio
The positive delta portfolio is a mid to long-term strategy that aims to take advantage of positive price movements in the market. It consists of various strategies designed to capture returns from the appreciation of assets. Here is an overview of the strategy and its key components:
Introduction to positive delta strategies
Positive delta strategies involve buying assets or options with a positive delta, which means they increase in value as the price of the underlying asset rises. These strategies aim to generate profits from upward price movements.
LEAPS income grid real strategy
The LEAPS income grid real strategy is a positive delta strategy that utilizes long-term equity anticipation securities (LEAPS) options. It involves buying LEAPS calls on dividend-paying stocks and selling shorter-term calls against them. By collecting dividends and option premiums, this strategy aims to generate consistent income.
Investing in index ETFs
Investing in index ETFs is another way to implement the positive delta strategy. Index ETFs track specific market indices and provide exposure to a diversified portfolio of stocks. By investing in index ETFs, traders can capture broad market returns and benefit from positive market movements.
Selecting stocks for long-term growth
Another component of the positive delta portfolio is investing in individual stocks for long-term growth. Traders can conduct fundamental and technical analysis to identify stocks with growth potential and positive market outlooks. By selecting stocks wisely, traders aim to generate capital appreciation over time.
By incorporating positive delta strategies into their portfolio, traders can position themselves to benefit from upward price movements and potentially achieve their long-term investment goals.
Allocation and Risk Management
Determining the optimal allocation and implementing effective risk management strategies are vital aspects of constructing and maintaining an options portfolio. Here are some considerations for allocation and risk management:
Determining the optimal allocation
The allocation of funds to different option strategies depends on individual preferences, investment goals, and risk tolerance. Traders should consider diversifying their portfolio by allocating funds to strategies that offer varying risk-reward profiles and potential returns.
Rebalancing your options portfolio
Regularly reviewing and rebalancing your options portfolio is crucial to maintain an optimal allocation. Market conditions and the performance of different strategies may change over time, requiring adjustments to ensure that the portfolio remains aligned with your objectives.
Monitoring and adjusting risk exposure
Monitoring and managing risk exposure is essential in options trading. Traders should regularly assess the risk associated with each strategy and implement measures to mitigate potential downside risks. This can include adjusting positions, hedging, or adjusting stop-loss orders.
Using stop-loss orders
Stop-loss orders can be useful tools to manage risk and limit potential losses. By placing stop-loss orders on options positions, traders can automatically sell or buy back options if certain price levels are reached. This helps protect against excessive losses and ensures disciplined risk management.
By allocating funds effectively and implementing robust risk management strategies, traders can mitigate potential losses and maximize the potential for returns in their options portfolio.
Factors Affecting Option Prices
Several factors influence the prices of options. Understanding these factors is crucial for options traders to make informed decisions. Here are some key factors affecting option prices:
Intrinsic value vs extrinsic value
The price of an option consists of two components: intrinsic value and extrinsic value. Intrinsic value is the difference between the strike price and the current price of the underlying asset. Extrinsic value represents the value attributed to factors such as time, volatility, and interest rates.
Option Greeks and their impact
Option Greeks are mathematical measurements used to quantify the sensitivity of option prices to changes in various factors. The main Option Greeks include Delta, Gamma, Theta, Vega, and Rho. Delta measures the change in option price for a $1 change in the underlying asset, Gamma measures the change in Delta for a $1 change in the underlying asset, Theta measures the time decay of an option, Vega measures the sensitivity to changes in implied volatility, and Rho measures the sensitivity to changes in interest rates.
Implied volatility and its role
Implied volatility is a measure of the market’s expectations for future price fluctuations of the underlying asset. It represents the perceived level of risk and uncertainty. Higher implied volatility results in higher option prices, as options become more valuable due to the increased potential for larger price movements.
Time decay and its effect
Time decay, also known as theta, refers to the reduction in the value of an option as time passes. As an option approaches its expiration date, theta increases, and the option loses value at an accelerating rate. Time decay can significantly impact the profitability of options, especially those with a short time until expiration.
By understanding the factors affecting option prices, traders can analyze and make more informed decisions regarding option selection, timing, and risk management.
Conclusion
Constructing an options portfolio requires careful consideration of various factors, including investment goals, risk tolerance, and market outlook. By diversifying strategies and allocating funds accordingly, traders can optimize their potential for profits while effectively managing risk.
Tailoring strategies to individual preferences and market conditions enables traders to adapt to different situations and market environments. Continued learning and adaptation are key to maintaining a successful options portfolio, as markets and strategies evolve over time.
With a comprehensive understanding of different options strategies and effective risk management techniques, traders can navigate the options market with confidence and potentially achieve their financial objectives.